Twitter for election forecasts: a Joint Machine Learning and Complex Network approach applied to an italian case study
Accepted for poster presentation at the International Conference on Computational Social Science, Helsinki, Finland, 8–11 June 2015 [1]. More details here [2].
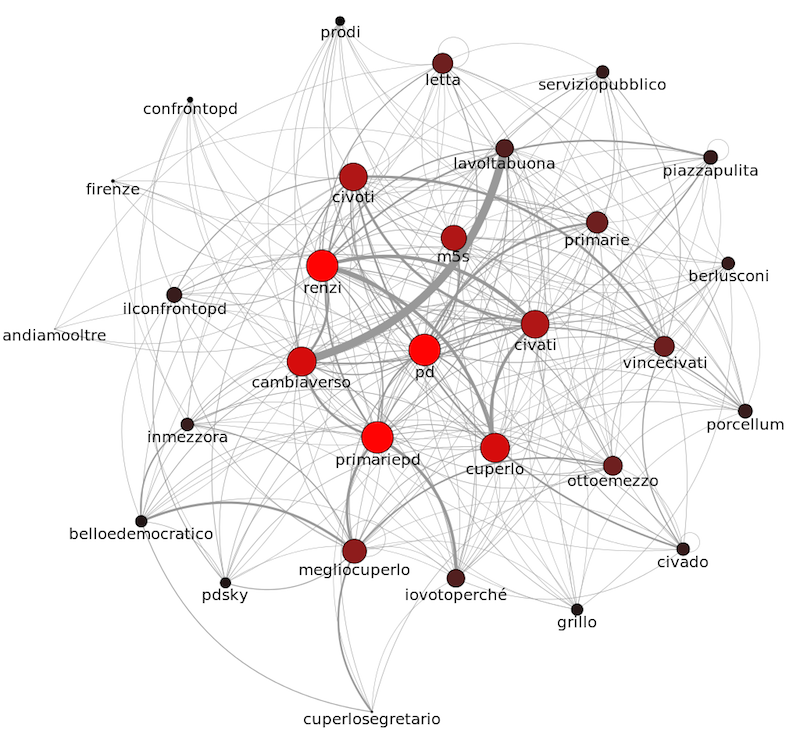
Abstract. Several studies have shown how to approximately predict real-world phenomena, such as political elections, by analyzing user activities in micro-blogging platforms. This approach has proven to be interesting but with some limitations, such as the representativeness of the sample of users, and the hardness of understanding polarity in short messages. We believe that predictions based on social network analysis can be significantly improved by exploiting machine learning and complex network tools, where the latter provides valuable high-level features to support the former in learning an accurate prediction function.
References
[1] Mauro Coletto, Claudio Lucchese, Salvatore Orlando, Raffaele Perego, Alessandro Chessa, and Michelangelo Puliga. Twitter for election forecasts: a joint machine learning and complex network approach applied to an italian case study. In IC2S2 ’15: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Social Science, 2015.
[2] Mauro Coletto, Claudio Lucchese, Salvatore Orlando, Raffaele Perego, Alessandro Chessa, and Michelangelo Puliga. Twitter for election forecasts: a joint machine learning and complex network approach applied to an italian case study. ISTI 2015-TR-009: Poster accepted at ICCSS 2015, 2015.
